Radio Observations of Tidal Disruption Events Around Direct Collapse Black Holes at Cosmic Dawn
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59973/emjsr.113Keywords:
quasars:general, dark ages, galaxies:high-redshift, first stars, black hole physics, early universeAbstract
Primordial haloes immersed within intermediate Lyman-Werner (LW) UV backgrounds are theorised
to be the seeds of supermassive primordial stars (SMSs) that could be the origin of the first quasars in our universe. Only extreme levels of LW fluxes however will destroy the molecular hydrogen H2 in these haloes, resulting in much less massive stars in the early stages of our universe. This investigation considers the collapse in haloes within weaker LW background that were much more common in the primordial universe, and allowed for the survival of some H2 within these haloes. The survival of H2 along with Tvir ∼ 104 K allows the atomic cooling of H2 to begin, triggering the baryonic collapse within these haloes. These flows are predicted to result in SMSs on the order of a few × 105 M⊙ before collapsing to a DCBH due to general relativistic instabilities within their cores. The stars formed through these mechanisms could be the origin seeds of intermediate mass black holes found within dwarf galaxies today, or even create a secondary tier of less massive but still highly luminous quasars at a redshift z > 7. Some of these stars form in binaries and small clusters, raising the possibility of future detections of gravitational waves from BH mergers by LISA. This investigation considers the tidal disruption events (TDEs) of lower mass Pop III stars that form within the nuclear accretion disc of these DCBHs, the potential observation of these TDE afterglows in the radio, and the
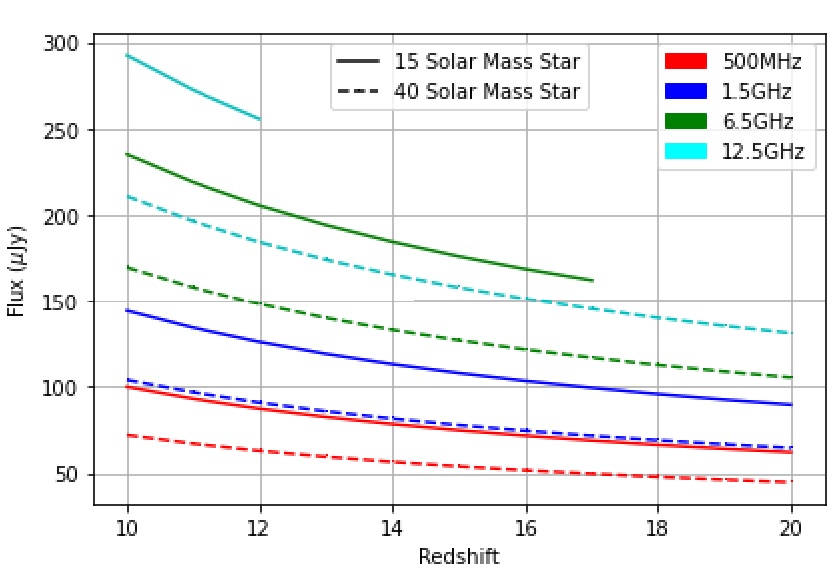
subsequent identification of their host DCBHs. We find that the radio observation of the afterglow of 15 M⊙ and 40 M⊙ TDEs due to 104 M⊙ DCBHs would be visible up to z = 20 by SKA and ngVLA.
References
Mortlock D. J., et al., 2011, Nature, 474, 616.
Matsuoka Y., et al., 2019, ApJ, 872, L2.
Yang J., et al., 2020, ApJ, 897, L14.
Wang F., et al., 2021, ApJ, 907, L1.
Fan X., Ba nados E., Simcoe R. A., 2023, ARAA, 61, 373.
Bogdan A., et al., 2023, doi:10.48550/arXiv.2305.15458, p. arXiv:2305.15458.
Maiolino R., et al., 2023, arXiv e-prints, p. arXiv:2305.12492.
Chandrasekhar S., 1964, ApJ, 140, 417.
Yue B., Ferrara A., Salvaterra R., Xu Y., Chen X., 2014, MNRAS, 440, 1263.
Dijkstra M., Ferrara A., Mesinger A., 2014, MNRAS, 442, 2036.
Agarwal B., Smith B., Glover S., Natarajan P., Khochfar S., 2016, MNRAS, 459, 4209.
Latif M. A., Bovino S., Grassi T., Schleicher D. R. G., Spaans M., 2015, MNRAS, 446, 3163.
Haemmerl Al’ L., 2021, Astronomy amp; Astrophysics, 650, A204.
Becerra F., Greif T. H., Springel V., Hernquist L. E., 2014, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 446, 2380ˆa A S2393.
Incatasciato A., Khochfar S., O A sorbe J., 2023, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 522, 330.
Spinoso D., Bonoli S., Valiante R., Schneider R., Izquierdo-Villalba D., 2022, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 518, 4672.
Regan J. A., Downes T. P., 2018, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 478, 5037ˆa A S5049.
Hosokawa T., Yorke H. W., Inayoshi K., Omukai K., Yoshida N., 2013, ApJ, 778, 178.
Umeda H., Hosokawa T., Omukai K., Yoshida N., 2016, ApJ, 830, L34.
Woods T. E., Heger A., Whalen D. J., Haemmerl e L., Klessen R. S., 2017, ApJ, 842, L6.
Haemmerl e L., Woods T. E., Klessen R. S., Heger A., Whalen D. J., 2018, MNRAS, 474, 2757.
Woods T. E., Patrick S., Whalen D. J., Heger A., 2021a, arXiv e-prints, p. arXiv:2112.09142.
Woods T. E., Patrick S., Elford J. S., Whalen D. J., Heger A., 2021b, ApJ, 915, 110.
Herrington N. P., Whalen D. J., Woods T. E., 2023, MNRAS, 521, 463.
Di Matteo T., Khandai N., DeGraf C., Feng Y., Croft R. A. C., Lopez J., Springel V., 2012, ApJ, 745, L29.
Di Matteo T., Croft R. A. C., Feng Y., Waters D., Wilkins S., 2017, MNRAS, 467, 4243.
Huang K.-W., Di Matteo T., Bhowmick A. K., Feng Y., Ma C.-P., 2018, MNRAS, 478, 5063.
Tenneti A., Di Matteo T., Croft R., Garcia T., Feng Y., 2018, MNRAS, 474, 597.
Spinoso D., Bonoli S., Valiante R., Schneider R., Izquierdo-Villalba D., 2022, Monthly.
Valentini M., Gallerani S., Ferrara A., 2021, MNRAS, 507, 1.
Lupi A., Haiman Z., Volonteri M., 2021, MNRAS, 503, 5046.
Latif M. A., Whalen D. J., Khochfar S., Herrington N. P., Woods T. E., 2022a, Nature, 607, 48.
Hirano S., Hosokawa T., Yoshida N., Umeda H., Omukai K., Chi- aki G., Yorke H. W., 2014, ApJ, 781, 60.
Hirano S., Hosokawa T., Yoshida N., Omukai K., Yorke H. W., 2015, MNRAS, 448, 568.
Whalen D., Abel T., Norman M. L., 2004, ApJ, 610, 14.
Kitayama T., Yoshida N., Susa H., Umemura M., 2004, ApJ, 613, 631.
Alvarez M. A., Wise J. H., Abel T., 2009, ApJ, 701, L133.
Whalen D. J., Fryer C. L., 2012, ApJ, 756, L19.
Smith B. D., Regan J. A., Downes T. P., Norman M. L., O’Shea B. W., Wise J. H., 2018, MNRAS, 480, 3762.
Johnson J. L., Whalen D. J., Li H., Holz D. E., 2013, ApJ, 771, 116.
Devecchi B., Volonteri M., 2009, ApJ, 694, 302.
Latif M. A., Omukai K., Habouzit M., Schleicher D. R. G., Volon- teri M., 2016, ApJ, 823, 40.
Sakurai Y., Yoshida N., Fujii M. S., Hirano S., 2017, MNRAS, 472, 1677.
Reinoso B., Schleicher D. R. G., Fellhauer M., Klessen R. S., Boekholt T. C. N., 2018, AA, 614, A14.
Boekholt T. C. N., Schleicher D. R. G., Fellhauer M., Klessen R. S., Reinoso B., Stutz A. M., Haemmerl e L., 2018, MNRAS, 476, 366.
Smidt J., Whalen D. J., Johnson J. L., Surace M., Li H., 2018, ApJ, 865, 126.
Latif M. A., Khochfar S., 2020, MNRAS, 497, 3761.
Zhu Q., Li Y., Li Y., Maji M., Yajima H., Schneider R., Hernquist L., 2022, MNRAS, 514, 5583.
Whalen D. J., Surace M., Bernhardt C., Zackrisson E., Pacucci F., Ziegler B., Hirschmann M., 2020, ApJ, 897, L16.
Surace M., et al., 2018, ApJ, 869, L39.
Wang L., et al., 2017, arXiv:1710.07005.
Rees M. J., 1988, Nature, 333, 523.
Evans C. R., Kochanek C. S., 1989, ApJ, 346, L13.
Hills J. G., 1975, Nature, 254, 295.
Reg os E., Vink o J., Stermeczky Z. V., 2021, ApJ, 909, 64.
Kashiyama K., Inayoshi K., 2016, ApJ, 826, 80.
Wright E. L., 2006, PASP, 118, 1711.
Planck Collaboration et al., 2020, AA, 641, A6.
Latif M. A., Aftab A., Whalen D. J., 2024, arXiv e-prints, p. arXiv:2401.07910.
Hirschmann M., Dolag K., Saro A., Bachmann L., Borgani S., Burkert A., 2014, MNRAS, 442, 2304.
Witstok J., et al., 2023, Nature, 621, 267.
Observatory S., 2024, Scientific Timeline — SKAO, https://www. skao.int/en/science-users/159/scientific-timeline.
ngVLA 2024, Project Timeline, https://ngvla.nrao.edu/.
Downloads
Published
Versions
- 2024-07-11 (2)
- 2024-07-11 (1)
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nathan Herbert

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.