A Machine Learning Approach to Measuring Time Delays in Microlensed Type la Supernovae
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59973/emjsr.320Keywords:
Machine Learning, Supernovae, Microlensing, light-curvesAbstract
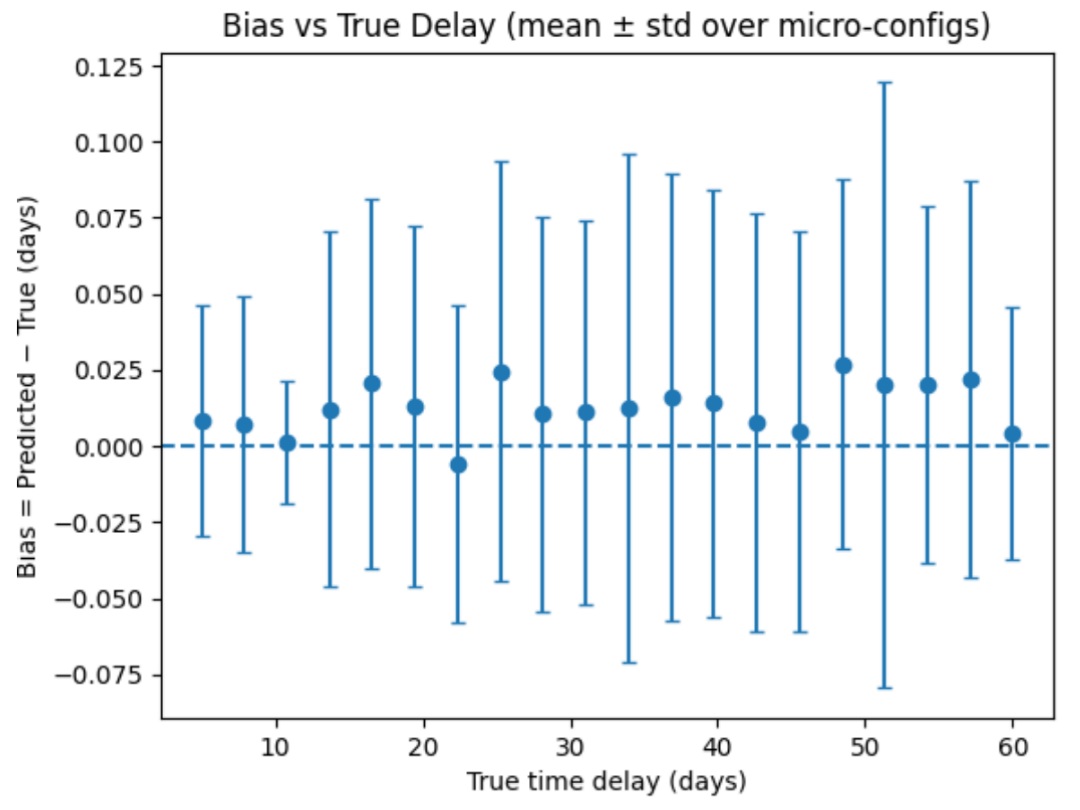
The discrepancy between early and late-Universe measurements of the Hubble constant, commonly referred to as the Hubble tension, remains one of the most significant open problems in modern cosmology. Strongly-lensed Type Ia supernovae provide a promising and independent probe of the cosmic expansion rate through time-delay cosmography, but their practical application is hindered by microlensing distortions and limited observational cadence. In this work, we present a machine-learning–based method for estimating time delays in microlensed Type Ia supernova light curves. Using realistically simulated lensed supernova datasets, we train and evaluate a Random Forest regression model to recover time delays between unresolved image pairs. We show that data-driven approaches can mitigate microlensing-induced biases relative to traditional cross-correlation methods and recover delays with improved robustness under challenging observational conditions. While this study does not perform a full cosmological inference, the results demonstrate the potential role of machine-learning techniques in future time-delay cosmography pipelines aimed at addressing the Hubble constant tension.
References
S. Sibirrer, Strong Gravitational Lensing: Basic Concepts, lecture notes, available at https://github.com/sibirrer/strong_lensing_lectures/blob/main/Lectures/lensing_basics_I.ipynb, accessed January 2026.
M. Bartelmann and P. Schneider, “Weak gravitational lensing,” Physics Reports, Vol. 340, Nos. 4–5, pp. 291–472, 2001, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0370-1573(00)00082-X, accessed January 2026.
S. Huber, S. H. Suyu, D. Ghoshdastidar, S. Taubenberger, V. Bonvin, J. H. H. Chan, M. Kromer, U. M. Noebauer, S. A. Sim, and L. Leal-Taix´e, “HOLISMOKES – VII. Time-delay measurement of strongly lensed Type Ia supernovae using machine learning,” Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 658, A157, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202141956, accessed January 2026.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Harry Nsubuga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.