Conjecture : The Theory of Everything is Embodied by Fundamental Replicators (Femes)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59973/ipil.101Keywords:
Fundamental Replicators , Femes, Computation, Evolutionary theory, Constructor theoryAbstract
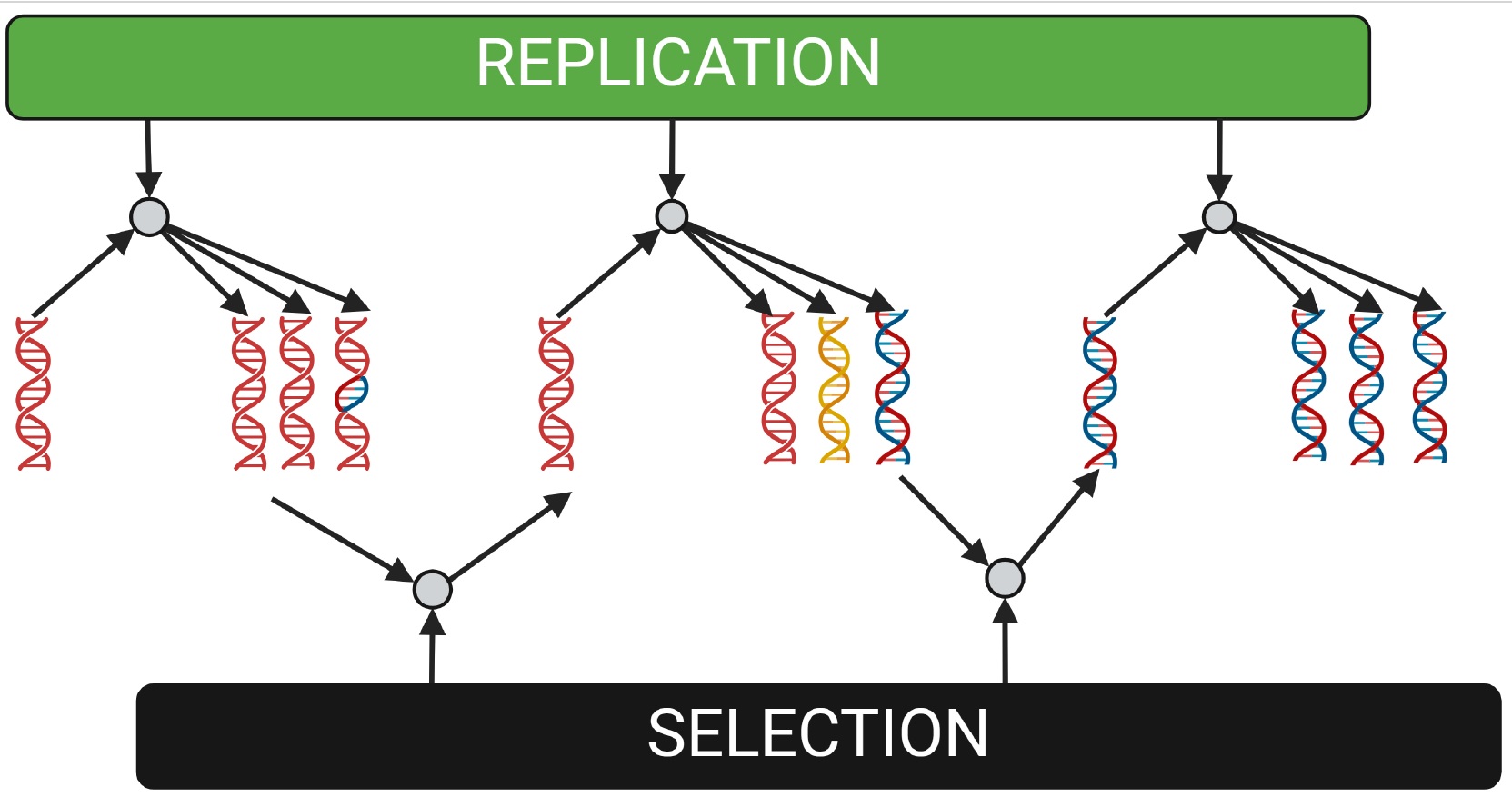
This paper conjectures that fundamental reality, taken to be an interacting system composed of discrete information, embodies replicating information structures called femes. These femes are posited to interact to cause the laws of physics. We therefore extend Universal Darwinism to propose the existence of four abstract replicators: femes, genes, memes, and temes. We firstly consider the problem of fine-tuning, and problems with current solutions. A detailed background section outlines key principles from physics, computation, evolutionary theory, and constructor theory. The conjecture is then provided in detail, along with five falsifiable predictions.
References
Stephen Wolfram. A Project to Find the Fundamental Theory of Physics. Wolfram Media, 2020.
John D. Barrow and Frank J. Tipler. The Anthropic Cosmological Principle. Oxford University Press, 1986.
Kurt Godel. On formally undecidable propositions. Placeholder for Journal, Placeholder:Placeholder, 1931.
Alan Turing. On computable numbers, with an application to the entscheidungs problem. Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, 2(42):230–265, 1936. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1112/plms/s2-42.1.230
David Deutsch. The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the World. Penguin UK, 2011.
David Deutsch and Chiara Marletto. The Constructor Theory of Information. Arxiv, 2012.
David Deutsch. Constructor theory. Synthese, 190(18):4331–4359, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-013-0279-z
David Deutsch. Constructor Theory. Oxford University Press, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2014.0540
Chiara Marletto. The science of can and can’t: A physicist’s journey through the land of counterfactuals. Viking, 2021.
YouTube. Glider. https://www.youtube.com/shorts/rnDHNtswypE, 2024. Accessed: 2024-05-30.
David H Wolpert and William G Macready. The no free lunch theorem. IEEE Transactions, 1997. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.585893
John Von Neumann, Arthur W Burks, et al. Theory of self-reproducing automata. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5(1):3–14, 1966.
Richard Dawkins. The extended phenotype: The long reach of the gene. Oxford University Press, 2016.
Richard Dawkins. The selfish gene. Oxford university press, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781912281251
Richard W Hamming. Error detecting and error correcting codes. The Bell system technical journal, 29(2):147–160, 1950. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1950.tb00463.x
Lex Fridman and S James Jr. Gates. Jim gates: Supersymmetry, string theory and proving einstein right. YouTube, 2019. https://youtu.be/IUHkhB366tE?si= LBPVVuo-2Mco0XBjt=3536.
Melvin M Vopson, Serban Lepadatu. Second law of information dynamics. AIP Advances, 12(7), 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0100358
Abhishek Sharma, Daniel Czegel, Michael Lachmann, Christopher P Kempes, Sara I Walker, and Leroy Cronin. Assembly theory explains and quantifies selection and evolution. Nature, 622 (7982) : 321–328, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06600-9
Downloads
Published
Versions
- 2024-06-20 (2)
- 2024-06-12 (1)
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Thomas Bradley

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.















