Co-Located Centers: Observational Support for Displaced Supersolid Dark Matter as the Source of Spacetime Curvature
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59973/ipil.239Keywords:
Dark matter, Spacetime, GravityAbstract
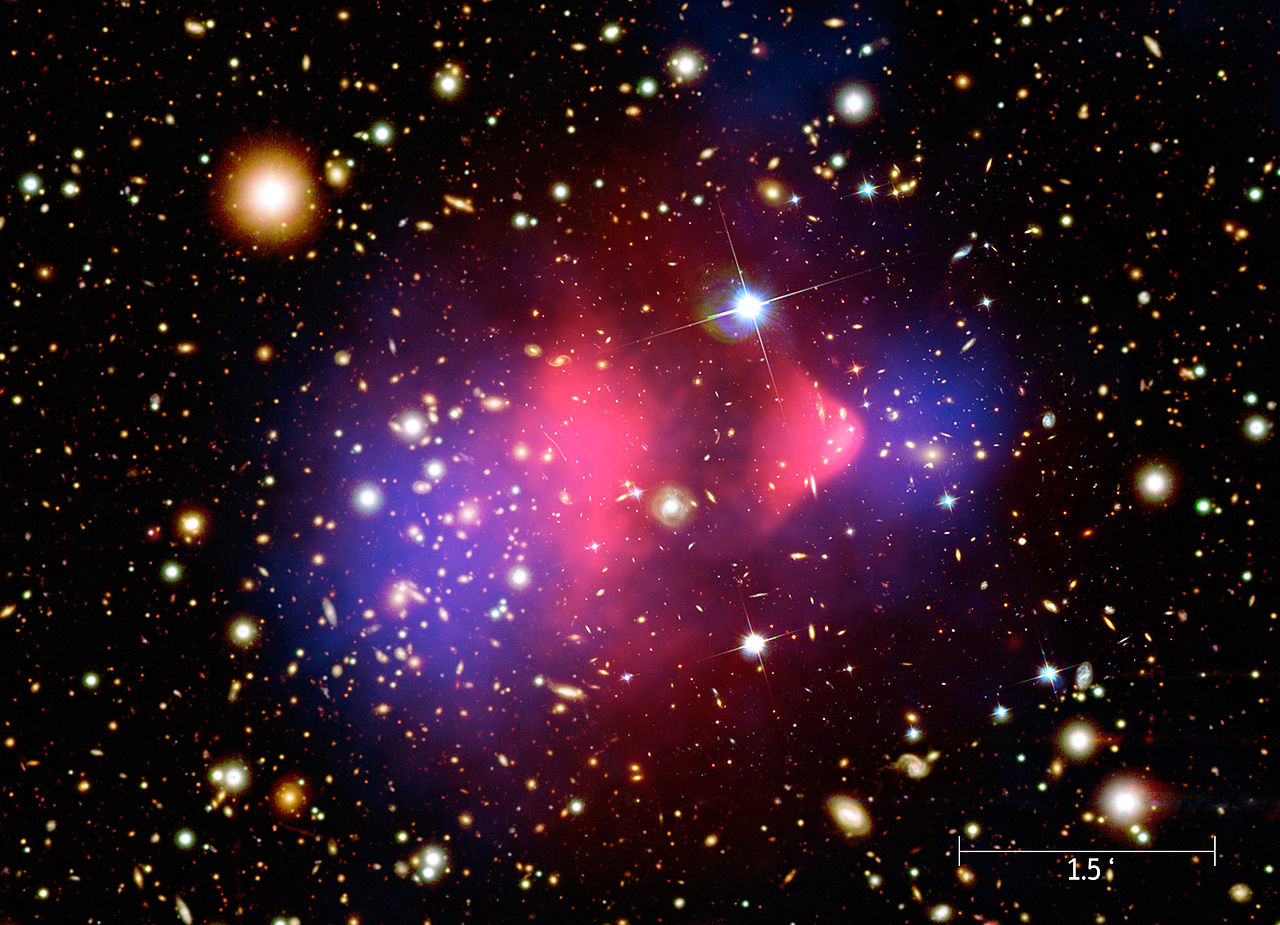
In a wide range of dynamically disturbed galaxy clusters, the center of the dark matter halo—as determined by non-lensing methods—coincides with the center of spacetime curvature as inferred by gravitational lensing. This co-location persists even in systems where the baryonic matter, including dominant gas components, is spatially displaced from the dark matter. We argue that this empirical pattern is not naturally explained by models in which spacetime curvature is generated by the total mass-energy content. Instead, it is more consistent with the notion that the dark matter halo is not an independent structure, but a displaced region of a gravitationally responsive medium—supersolid dark matter—displaced by the ordinary matter [1].
This interpretation accounts for both the observed co-location and the absence of any measurable baryonic influence on the curvature center.
References
Cavedon, M. (2025). Supersolid Dark Matter and the Fabric of Spacetime. IPI Letters, 3(2), O81-O85. https://doi.org/10.59973/ipil.197. DOI: https://doi.org/10.59973/ipil.197
Clowe, D., et al. ”A direct empirical proof of the existence of dark matter.” The Astrophysical Journal Letters 648.2 (2006): L109. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/508162
Bradac, M., et al. ”Strong and weak lensing united. II. Mass reconstruction of the merging galaxy cluster 1E 0657-56.” The Astrophysical Journal 652.2 (2006): 937–947. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/508601
Mahdavi, A., et al. ”A dark core in Abell 520.” The Astrophysical Journal 668.2 (2007): 806–814. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/521383
Jee, M. J., et al. ”A study of the dark core in A520 with Hubble Space Telescope: the mystery deepens.” The Astrophysical Journal 747.2 (2012): 96. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/747/2/96
Bradac, M., et al. ”Revealing the properties of dark matter in the merging cluster MACS J0025.4-1222.” The Astrophysical Journal 687.2 (2008): 959–967. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/591246
Merten, J., et al. ”Creation of cosmic structure in the complex galaxy cluster merger Abell 2744.” Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 417.1 (2011): 333–347. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19266.x
Medezinski, E., et al. ”CLASH:Weak-lensing shear-and magnification analysis of 20 galaxy clusters.” The Astrophysical Journal 817.1 (2016): 24. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3847/0004-637X/817/1/24
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Michael Cavedon

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.















